Optimizing the Laser Cutting Process: A Guide to Design File Preparation
Laser technology has revolutionized the manufacturing and design industry, allowing for precise and rapid cuts in a variety of materials. From prototyping to mass production, laser cutters have become an indispensable tool in many fields. However, to fully harness the potential of this technology, it is crucial to properly prepare design files. In this guide, we will explore the fundamentals of file preparation to optimize the cutting process with laser cutters.
Importance of File Preparation
Design file preparation is essential to ensure accurate and efficient results in the laser cutting process. Poorly prepared files can result in imperfect cuts, material waste, and longer production times. By following best practices in file preparation, these issues can be avoided, and the efficiency of the cutting process can be maximized.
Common File Formats
Before delving into best practices for file preparation, it is important to understand the most common file formats used in laser cutter design. Popular formats include:
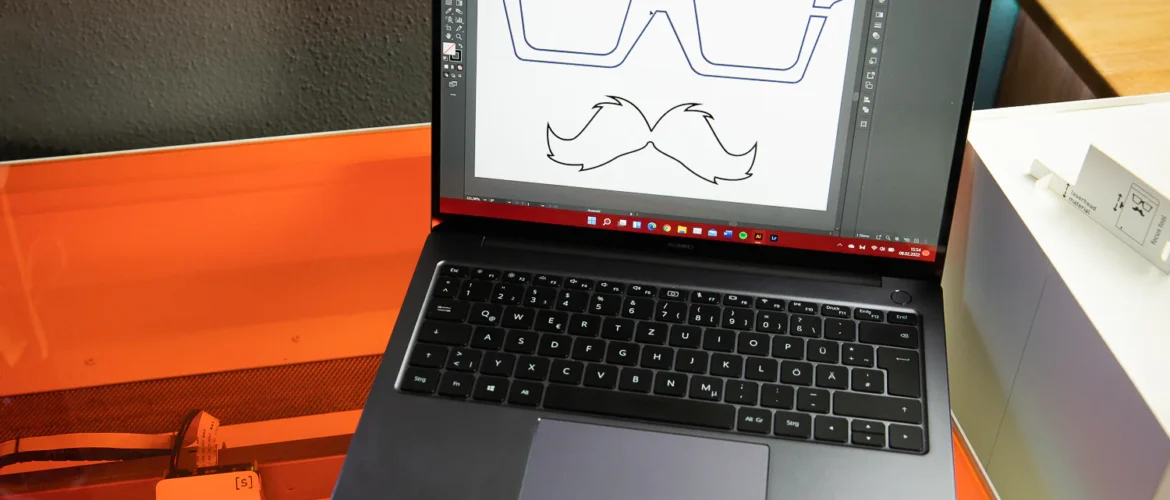
- Vector Formats: Vector files are ideal for laser cutting, as they are based on mathematical formulas that define shapes and lines. Common vector formats include SVG, AI (Adobe Illustrator), EPS, and DXF.
- Raster Formats: Although less ideal for laser cutting, raster files can be used for certain designs. These include formats such as PNG, JPG, and BMP. However, it is important to ensure that the resolution is high enough to maintain cutting quality.
Best Practices for File Preparation
- Use Suitable Design Software: To prepare design files for laser cutters, it is essential to use suitable design software. Adobe Illustrator, CorelDRAW, and Inkscape are popular options that support vector formats and provide specific tools for creating laser cutting files.
- Convert Texts to Outlines: When working with vector files, it is important to convert all texts to outlines. This ensures that the design does not rely on specific fonts and avoids compatibility issues when sending the file to the laser cutter.
- Define Cutting and Engraving Lines: It is crucial to distinguish between cutting lines and engraving lines in the design. Cutting lines indicate where the laser should cut the material completely, while engraving lines are used to mark or engrave the material without cutting it completely. Using different colors or line attributes facilitates this distinction.
- Optimize Piece Distribution: When preparing files for laser cutting, it is important to optimize the distribution of pieces on the material to minimize waste. Grouping similar pieces and adjusting their layout can help maximize material yield and reduce costs.
- Consider Cutting Tolerance: It is important to consider cutting tolerance when designing parts for laser cutters. The width of the laser beam and other factors can influence cutting accuracy, so it is recommended to leave additional space in joints and connections to ensure proper assembly.
- Check Scale and Dimensions: Before sending the file to the laser cutter, always verify the scale and dimensions of the design. Errors in scale can result in poorly cut or unusable parts, so it is important to ensure that everything is correctly sized.
- Export in Suitable Format: Once the design is ready, be sure to export it in the appropriate format compatible with the laser cutter. Consult the manufacturer’s specifications or service provider to ensure compatibility and cutting accuracy.
Advanced File Preparation Tools
In addition to the basic practices mentioned above, there are advanced tools and techniques that can further improve the file preparation process for laser cutters.
- Automated Optimization: Some design software and specialized tools offer automated optimization functions that can help maximize cutting efficiency and minimize material waste. These tools use advanced algorithms to calculate the optimal layout of pieces on the material.
- Cut Simulation: Before sending the design to the laser cutter, it is useful to perform a cut simulation to verify the accuracy and feasibility of the design. Some design software offers simulation tools that allow you to preview the cutting process and detect potential issues before production.
- Cutting Parameter Optimization: In addition to preparing the design, it is also important to optimize the cutting parameters in the laser cutter. This includes adjusting laser power, cutting speed, and other settings to ensure optimal results on different materials and thicknesses.
- Layer Management: When working with complex designs, layer management can facilitate organization and editing of the file. Using separate layers for cutting lines, engraving lines, and other elements can make the design easier to understand and modify.
Conclusion
Proper design file preparation is crucial for optimizing the laser cutting process. By following best practices and utilizing advanced tools, accuracy, efficiency, and quality can be ensured in laser cutting results. By mastering file preparation, designers and manufacturers can fully leverage this powerful technology, maximizing productivity and minimizing errors. Ultimately, proper file preparation is essential to unlock the full potential of laser cutters in a variety of industrial and creative applications.
You may also like